Brief introduction
E-billing enables the digital and automated transmission of invoice data to the Confederation. Invoices can either be emailed as a PDF file or be submitted as a structured dataset via a service provider. The Confederation processes the data electronically, which avoids manual logging errors and accelerates the process.
How e-billing works
With e-bills, all necessary invoice data is transmitted electronically from the biller to the bill recipient. This paperless process allows the information to be processed electronically at the recipient's end without it having to be imported manually into the systems. The workflow is shown in the diagram below and compared with the traditional process:
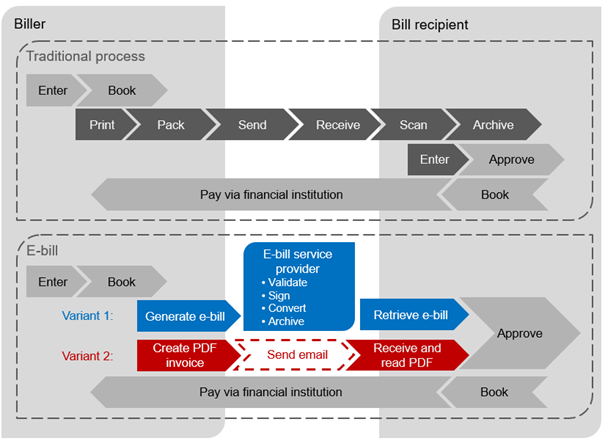
An e-bill can either be sent as a PDF file via email or be submitted as a structured dataset via a service provider. The recipient receives the e-bill and processes it electronically. The structured dataset can be imported directly, whereas the PDF file must be scanned. The e-bill is not paid until it has been approved by the bill recipient via his/her financial institution.
External links
- Forum for the promotion of business-to-business electronic invoicing: www.swissdigin.ch
- The eCH association promotes eGovernment standards: www.ech.ch
- Everything you need to know about the Unique Business Identification Number: www.uid.ch
- GS1 – The Global Language of Business: www.gs1.ch

